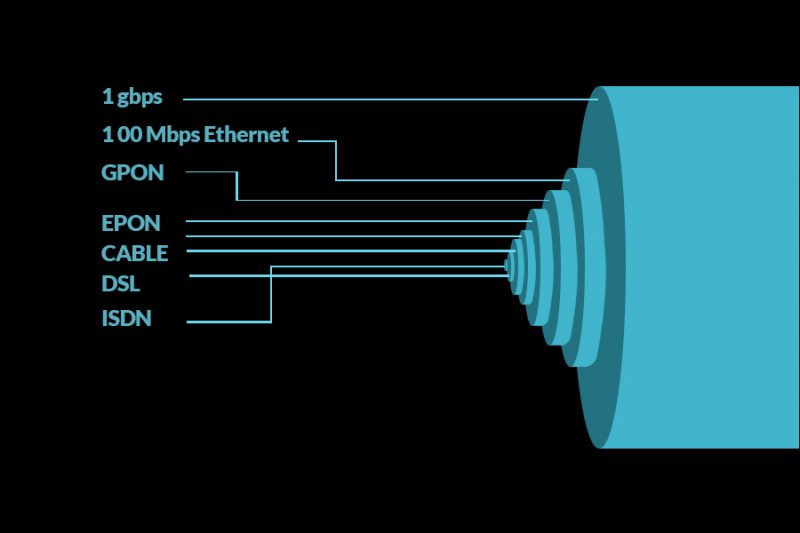
Bandwidth in cables refers to the range of frequencies used to transfer information through data cables. The broader the bandwidth, the more data can be carried respectively.
The bandwidth in cables is applicable to data cables where it’s looking at radio and audio frequencies Bandwidth is measured in cycles per second or frequency per unit of time. Usually you’ll find it quantified as Hertz (Hz). Below we’ll use the abbreviation MHz, it stands for Megahertz. 1 Megahertz is equivalent to 1 million Hertz.
A breakdown of data cable can be classified as follows:
- CAT 3 Cable = Up to 16 MHz
- CAT 4 Cable = Up to 20 MHz
- CAT 5 Cable = Up to 100 MHz
- CAT 6 Cable = Up to 250 MHz
- CAT 7 Cable = Up to 600 MHz